BBC research shows DAB is the most energy-efficient radio platform
11.11.2020 by WorldDAB
At last week’s General Assembly, the BBC’s Sustainability Data Scientist Chloe Fletcher presented the findings of a BBC study looking at the energy footprint of BBC radio.
Using the BBC’s listening figures from 2018, the research compared the energy consumption of the BBC’s radio stations across all analogue and digital platforms.
The research – which compared AM, FM, DAB, IP and DTV radio services – found that DAB radio services have the lowest energy consumption per device hour, and determined that in the long-run, retaining DAB and IP only would lead to the largest energy savings.
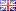
Annual energy consumption by radio platform
According to the results of the research, FM had the highest levels of energy consumptions, claiming around 31% of the total energy. AM had the lowest at 8%, while DAB had about 20%.
However, as pointed by Fletcher, not all platforms were used equally in 2018, and this particular figure did not take into account the usage of each individual platform, with FM and DAB having a much higher listening share than other platforms – particularly AM and DTV.
FM uses 40% more energy per hour than DAB
When looking at energy consumption levels per device per hour, the research indicated that DAB radio services have the lowest energy consumption compared to other platforms, at 9-Watt hours (Wh).
The study also found that FM radio services use approximately 40% more energy per hour than DAB – “mainly because of the higher power consumption of the FM transmitter network”, as well as the fact that “DAB radios tend to have a lower standby power on those devices” said Fletcher.
DAB and IP – the most efficient long-term solution
The research modelled a variety of scenarios to determine where exactly energy could be saved, and while most scenarios showed energy saving potential, retaining DAB and IP – and switching off analogue services and – led to the largest energy saving by far.
The study also underlined the importance of reducing our electronic devices standby energy consumptions, as these are the biggest contributors to the total energy consumption.

Chloe Fletcher speaking at the WorldDAB 2020 virtual General Assembly
Spreading the word
This work forms part of the BBC’s commitment to reducing the environmental footprint of media services and technology through the BBC Greener Broadcasting strategy.
By taking a system-wide approach, the BBC has highlighted the complexities across the radio chain and potential interventions to reduce the negative environmental impacts within it. The findings of this research are now being shared far and wide to educate the community and seek change through industry collaboration.
Posted in:
- British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) WorldDAB Member
- United Kingdom